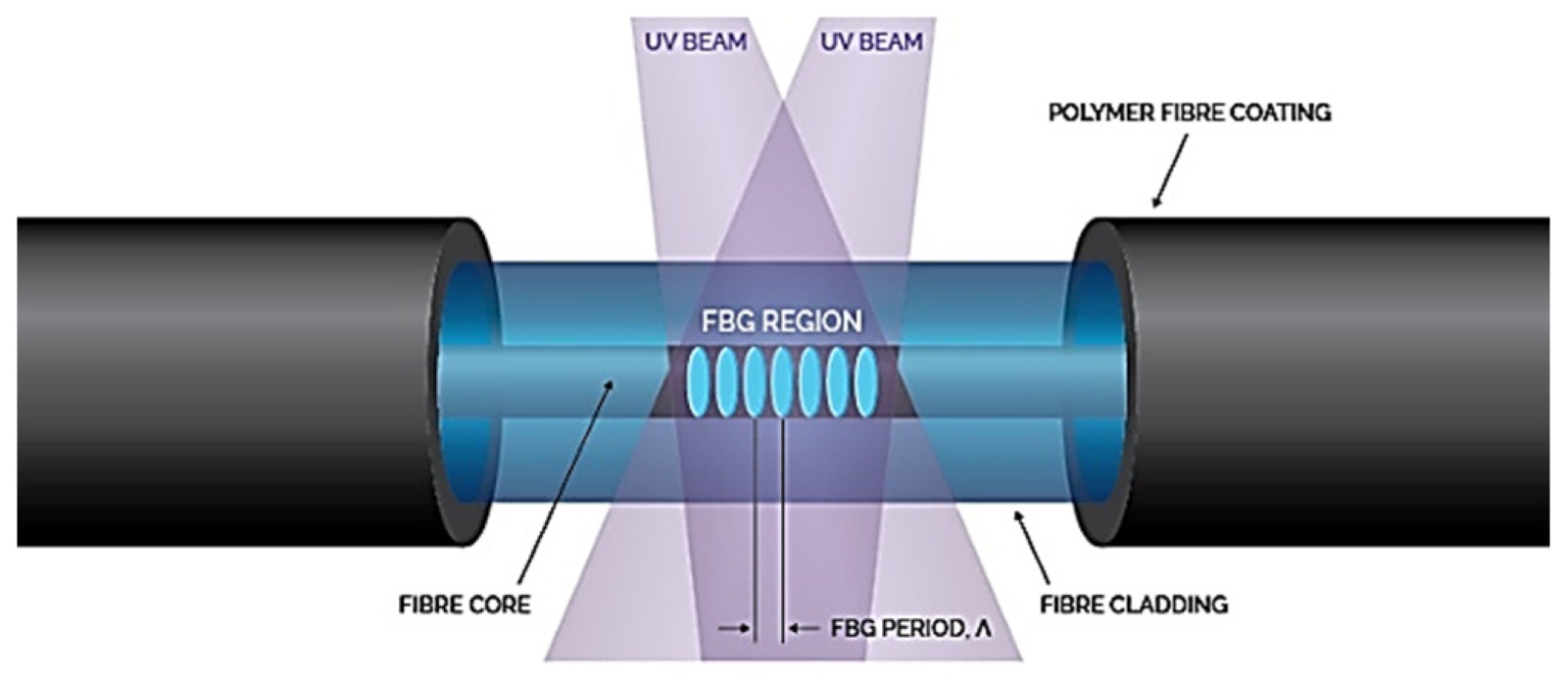
FBG
Fiber Bragg Gratings (FBGs) have emerged as highly effective sensors for detecting vibration, temperature, and strain. These sensors function by incorporating a periodic modulation of the refractive index within the core of an optical fiber. When broadband light is propagated through the FBG, a specific wavelength, known as the Bragg wavelength, is reflected. This wavelength is highly sensitive to changes in strain, temperature, and vibration, which alter the grating's period and refractive index. By monitoring shifts in the reflected Bragg wavelength, precise measurements of these physical parameters can be obtained. Furthermore, by placing multiple FBG's at different points along the fiber, zone based sensing can be achieved, allowing for distributed sensing along the length of the fiber. This makes FBG's very useful for structural health monitoring, and many other applications.